Our complex machines and facilities often contain critical systems and functions that cannot afford to fail. Regardless of whether the entire facility loses power, these systems must continue operating to ensure safety functions or support functions that guarantee control over the facility, for instance. Therefore, various types of backup systems are needed. One way to solve this issue is by utilizing battery-backed direct current (DC) as the control voltage for these functions. This way, the functions always have voltage available, even if the main power supply to the facility fails.
DC systems consist of components like circuit breakers, transformers, charging units, motor starting equipment, communication units, and, of course, batteries. These components are dimensioned based on the facility's requirements for battery type, voltage, power, and runtime.
DC systems are primarily used in industries such as oil and gas to protect and ensure the functionality of substations, control units, emergency pump systems, and fire suppression systems. Therefore, it's of utmost importance that these deliveries uphold the highest standards in terms of reliability and quality. Additionally, availability and user-friendliness must meet the stringent demands. These critical systems are often tested by our customers directly at Elektromontage to further enhance delivery assurance.
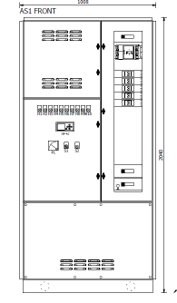
In the 24VDC systems, alternating current is supplied and then converted to 24VDC through the regulated battery charging system within the control cabinet. Backup batteries are monitored and charged from the same units that provide the control voltage to the consumers. This enables a seamless transition to battery operation in the event of a disruption in the alternating current supply. It's important to note that this is not a conventional Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) but rather a battery-backed DC system, specifically suited for control cabinets for turbines and similar applications. These systems are designed to operate on 24VDC under normal conditions.
Similarly, a 125VDC system functions in the same way. This voltage is used, for example, as the control voltage for the coils of circuit breakers in substations and as emergency power for other functions, such as direct current motors for oil pumps providing lubrication to the turbine shaft. These safety functions must ensure that a turbine can undergo a controlled shutdown without risking the costly equipment.